The need for an efficient context layer in the AI Era
Memory is the fundamental substrate of every system you build. Memory is a subset of context that not only outlines the duration of remembering discussions or acquired knowledge but also influences what the system considers pertinent, how it evolves over time, and how reliably it functions throughout interactions.
Throughout the years, AI agents have transformed from basic chatbots into extensive workflows: programming assistants, research applications, sales helpers, customer support teams, coding partners, and independent task performers. If we can limit the model size or processing capacity of these agents, then their performance won't increase with additional parameters - it scales with memory.
However, raw memory is not the same as effective context. As interaction histories expand from thousands to millions of tokens, the challenge transitions from storage to retrieval. Merely filling a model's context window with all previous interactions weakens its reasoning abilities, adding noise and raising the likelihood of hallucinations.
Genuine intelligence necessitates a Context Layer, a framework that transforms extensive collections of 'Memory' into the exact, pertinent 'Context' an agent requires for the present nanosecond. The distinction between a good agent and an exceptional one lies not only in the model but in the skill to find the correct needle in the haystack consistently.
But in a landscape flooded with memory solutions, bold claims aren't enough - we need proof. To truly understand the impact of an efficient context layer, we must look at the data.
Benchmarks: Evaluating the Context Layer
Assessing the quality of memory and context systems will differentiate basic implementations from genuinely intelligent, context-aware applications. Memory benchmarks act as standardised tests that assess the efficiency of memory layers in storing, retrieving, and contextualising information throughout conversations and interactions.
These benchmarks are crucial as they directly influence the efficiency of AI agents in real-world applications. Whether you're creating a customised assistant, a sales automation tool, or a customer success solution, the effectiveness of your memory system influences the intelligence with which your agents function. A nuanced method will be employed to assess two aspects: conversational memory and the evaluation of long-term memory.
LongMemEval: Testing Memory Systems Across Time and Sessions
Long-term memory assessment (LongMemEval) evaluates the effectiveness of memory systems over prolonged durations, various conversation sessions, and changing user scenarios. The system's capability to preserve, refresh, and access information is evaluated as relationships grow stronger, preferences evolve, and knowledge builds over weeks or months of engagement.
The assessment framework primarily investigates six essential dimensions:
- Single-Session User Facts: Capturing and recalling explicit user statements within one conversation
- Single-Session Assistant Facts: Retaining information the AI agent itself provided
- Single-Session Preferences: Understanding and remembering user likes, dislikes, and choices
- Knowledge Updates: Correctly updating memories when new information contradicts or refines previous facts
- Temporal Reasoning: Understanding time-based context and sequencing of events
- Multi-Session Continuity: Maintaining coherent memory across separate conversation instances
Let’s examine this multiple-session engagement:
Session 1 (January):
User: "I’m preparing for a marathon in April." "My present speed is 10 minutes for each mile."
Session 2 (February):
User: "Fantastic news! "I've enhanced my speed to 8:30 for each mile."
Session 3 (March):
"Is it necessary to modify my training regimen based on my advancements?"
Perfect Response from Extended Memory System:
“Certainly! Your speed has markedly increased from 10:00 to 8:30 per mile since January - that's a fantastic advancement with your marathon in April nearing. Considering this 15% enhancement, it would be wise to revise your target completion time and add more tempo runs to sustain this progress.”
Benchmark Performance (LongMemEval): Alchemyst AI vs. The competition
Our LongMemEval assessment compares four major memory platforms - Alchemyst, SuperMemory, Zep, and Hindsight GPT OSS 120B across six evaluation categories, measuring both performance accuracy and cost efficiency.
For Single-Session assessment, Alchemyst delivers accuracy competing with the top tier. Alchemyst performs with nearly 90% accuracy while giving a substantial cost advantage. In tracking AI response across a single session (55 test cases) Alchemyst matches Supermemory’s performance while costing 99.7% less and dramatically outperforms the expensive Zen option.
Knowledge update test measures how well systems update memories when users correct or refine previous statements. A low score here does not imply that this is a design flaw - infact this was expected with the base layer’s implementation, which we evaluated for LongMemEval. With Alchemyst, you can implement domain-specific knowledge update measures, since knowledge updates are covered as a part of agentic logic, not part of the data itself. The inherent connectivity of data between data points can be business-specific, which is why we leave it to the business user to implement that. This allows us to be flexible by avoiding the pitfalls of updates that might violate business logic.
Alchemyst delivers near-SuperMemory performance in temporal reasoning, which measures how much a system can understand the time and sequence dependencies. Multi-session continuity is where Alchemyst is seen to outperform supermemory, which serves as a remarkable achievement in the aspect of long-term memory.
ConvoMem: Pushing evidence-based contextualization for LLM responses to the edge
Conversational memory refers to an AI assistant's ability to draw on information from previous conversations to generate replies that are more informative, logical, and appropriate to the situation. It serves as a broad concept that includes semantic, episodic, and procedural memory while steering clear of strict category distinctions.
It closely connects with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), since both rely on acquiring relevant context from a saved text corpus to improve answers. In conversational memory, the collection of information includes past discussions, with the primary aim being to make dialogue systems progressively more natural, coherent, and efficient over time.
A context layer provider or developer of memory systems would choose to benchmark using ConvoMem for several strategic and technical reasons that differentiate it from previous benchmarks like LongMemEval or LoCoMo.
The primary reasons to use this benchmark include:
- Statistical Power and Reliability: ConvoMem’s 75k+ dataset is 150x larger than LongMemEval, narrowing confidence intervals to under ±2%, unlike smaller benchmarks where error margins can swing as high as ±40%.
- Testing Multi-Message Synthesis: Distributes evidence across 1–6 messages to test true information assembly, moving beyond shallow keyword retrieval.
- Evaluation of Implicit Reasoning: Evaluates "ambient awareness" by testing if systems recall user circumstances (like a past injury) without explicit reminders.
- Identifying Architectural Transition Points: Identifies specific performance "cliffs" (e.g., at 150 conversations) to help developers pinpoint exactly when to switch from long-context windows to RAG.
- Methodological Consistency: Uses a unified generation pipeline for all data, preventing models from gaming the test by detecting stylistic differences in synthetic text.
- Optimization of Model Selection: Demonstrates that medium-tier models often match premium performance for memory tasks, validating cost-effective context layer implementations.
The theoretical base is built on three key elements:
- Extraction: Recognising significant details from unstructured conversations (user preferences, declared facts, suggested context)
- Indexing: Structuring this data to allow rapid, semantically meaningful access.
- Retrieval: Accessing the appropriate memories during a query by considering semantic relevance and the context of the conversation.
Suppose a user engages in this dialogue with an AI assistant:
User: "I'm planning a trip to Japan in March. I'm vegetarian and love hiking."
Later in the conversation or even in a subsequent session, the user asks:
Query: "What should I pack for my trip?"
Optimal Response from Memory-Powered Agent:
"During your March visit to Japan, I suggest bringing layers due to fluctuating temperatures (5-15°C)." Since you enjoy hiking, pack a lightweight rain jacket; March can be wet. As a vegetarian, consider bringing some protein bars as a backup, although Japan is offering more excellent vegetarian choices in urban areas."
Benchmarking context providers on ConvoMem
We have benchmarked all of the ConvoMem observations using the MemoryBench tool by SuperMemory.
Our comprehensive evaluation reveals significant performance differences across memory systems.
Accuracy: The Most Critical Metric
Alchemyst Standard dominates with 80% accuracy, while Alchemyst Fast follows with 70%, and SuperMemory attained just 50%. In practical terms, this implies that Alchemyst can remember user preferences and facts with greater consistency. It ensures a smooth conversation without requiring the user to restate anything.
Retrieval Quality: Precision Matters
Metrics like Hit@K, Recall, MRR, and NDCG measure how effectively the system identifies the correct memory and whether it appropriately ranks that memory when multiple past facts are available. In this case, Alchemyst Standard excels, reaching a Hit@K of 80% and demonstrating markedly superior MRR and NDCG compared to Alchemyst Fast and SuperMemory. The rapid version still stays competitive, surpassing SuperMemory in various recall measurements.
When we assess these outcomes against mem0, the trend still holds. mem0 generally functions within the ~55–60% accuracy bracket on ConvoMem evaluation tasks, showing significantly increased latency as histories extend and ranking quality diminishes more rapidly during extended conversations. This positions mem0 within the same performance category as SuperMemory.
Latency: Speed meets Intelligence
Analyzing the latency distribution uncovers intriguing compromises. In search operations, SuperMemory leads with 893ms, closely trailed by Alchemyst Fast at 919ms, and Alchemyst Standard takes 1,467ms.
Most importantly for production deployments, Alchemyst excels in ingestion speed. This metric is vital in real-time scenarios, where discussions consistently create memories. It determines the speed at which a new conversational context is made searchable. Alchemyst Standard (1,385ms median) and Fast (1,389ms median) process memories over 2x quicker than SuperMemory's 2,976ms.
Conclusion
This indicates that Alchemyst not only retrieves memories but also identifies the most pertinent ones and correctly prioritises them while formulating the final response. That conduct is precisely what downstream roles such as customer service, research helpers, coaching agents, and copilots truly require.
Cheaper Context, Scalable Intelligence
In the current AI development landscape, engineering teams encounter an unjust dilemma: they can either create highly intelligent agents that are very expensive or more affordable agents that experience “amnesia.” This is due to the fact that performance increases with memory, and unit economics do as well.
The "Million Token" Impact
To understand the magnitude of this issue, we must look beyond a single user's monthly subscription fee to consider the cost of scale, specifically, the industry-standard price per 1 million tokens.
When we study the pricing patterns of leading competitors, the math shows a clear reality:
- Supermemory: As seen in their pricing tiers, the "Pro" plan charges $19/month for 3 million tokens processed, which is roughly $6.33 per million tokens.
- Zep: Their model relies on "credits," charging $25/month for 20,000 credits. 1 credit = 300 bytes = 300 characters ~= 100 tokens. In our analysis, this translates to an effective comparative price metric of roughly $12.50 per million tokens, nearly double that of Supermemory.
Alchemyst: In contrast, the architecture of Alchemyst is designed for efficient context-aware retrieval. The cost of our context search is about $0.061 per million tokens.
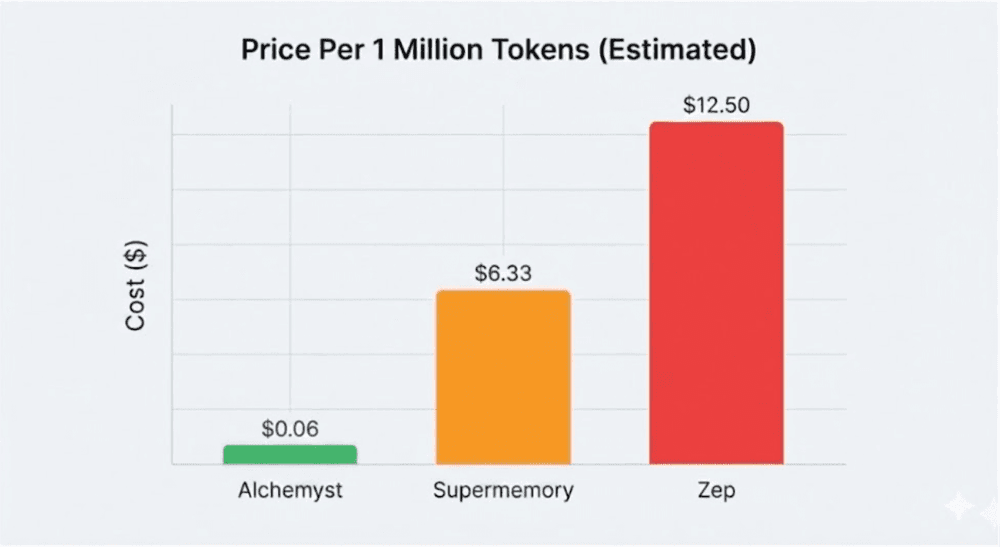
On paper, the difference of a few dollars may appear insignificant. However, when you scale an agent to thousands of users, the difference skyrockets.
The Efficiency Frontier: Defining the "Sweet Spot"
In the fields of economics and engineering, there exists a concept referred to as the "Pareto Frontier" or Efficiency Frontier. It displays the collection of best choices where enhancing one metric necessitates compromising another. In the field of AI memory, two key aspects are Performance (the effectiveness of the system’s recall) and Price (the operational cost).
Historically, developers were required to make a difficult trade-off. Achieving high recall and strong context retention necessitates a considerable commitment to robust, resource-demanding infrastructure. Yet, if you prioritised low expenses, you had to endure "lossy" memory, which forgets user information or fabricates details over extended durations. Many current solutions remain low on this curve, demonstrating inefficiency: they demand excessive fees for minimal performance.
Alchemyst fundamentally changes this dynamic. The subsequent analysis shows that Alchemyst is positioned precisely on the efficiency frontier. This is the "optimal point" where excellent performance and minimal expense coexist. We pushed the boundaries by enhancing the fundamental memory retrieval system. We don't merely balance the trade-off; we actually remove the penalty, enabling developers to utilise optimal recall capabilities without the typical linear cost increase associated.




